Environmental Issues in Italy
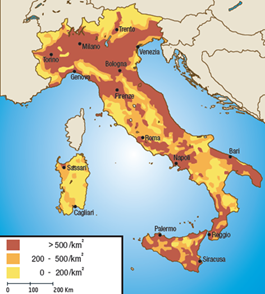
Italy is a peninsula predominantly hilly and mountainous, only 23% of territory is in plain, water resources are not evenly distributed (abundant in the north, scarce in the South), population is mainly concentrated in the plains, with widespread urban settlements (urban sprawl), which implies a considerable consume of arable land, within which industrial clusters, homogeneous for type of industry, have developed.
The fact that, within a certain area, there is a clusterization of Small and Medium Enterprises, engaged in the same industrial segment, has the advantage to have environmental impacts fairly homogeneous for that area, but, because the small size of the enterprises, technologies for reduction of emissions and pollutants may be too costly for the single enterprise.
Moreover, the combination of the wide variety of eco-systems with the huge number of industrial clusters, implies a wide number of types of environmental impacts and, therefore, of solutions for environmental protection.
That’s why, Italy developed the model of the “Ecologically-Equipped Productive Area” , where industrial factories are located in a system, that allows them to realize common infrastructures for environmental protection for the whole area.
This situation of geographic fragmentation for environmental issues and the need to build infrastructures, specific for the single areas, are perfectly integrated into the system of the public utility companies, that, because of the geographic responsibility limited to the City Administrations that are shareholders (with exclusion of the four public utility companies listed in the Stock Exchange), were able to design and build specific solutions.
Last, where industrial processes are particularly pollutants, enterprises are involved in financing and operating common infrastructures, through aggregation mechanisms (consortia, agencies for the industrial area, etc.)